Stargate concepts
Stargate is a framework used to customize all aspects of data access. It is deployed between client applications and a database to provide an abstraction layer that can be used to shape your data access to fit your application’s needs.
|
Notification of deprecation and schedule to remove
Cassandra 3.11 Persistence Backend - According to the Cassandra documentation, the 3.11 release is currently the "Previous Stable Version" scheduled for maintenance until 5.0 is released in mid-2023. Since Cassandra 3.11 has a dependency on Java 8, removal of the 3.11 persistence backend would allow the build of the coordinator modules to be updated to Java 11 (for Cassandra 4.x) and to use a Java 11 base Docker image. Thus, the Cassandra 3.11 persistence module is being deprecated and scheduled for removal in Stargate v3. |
Project architecture
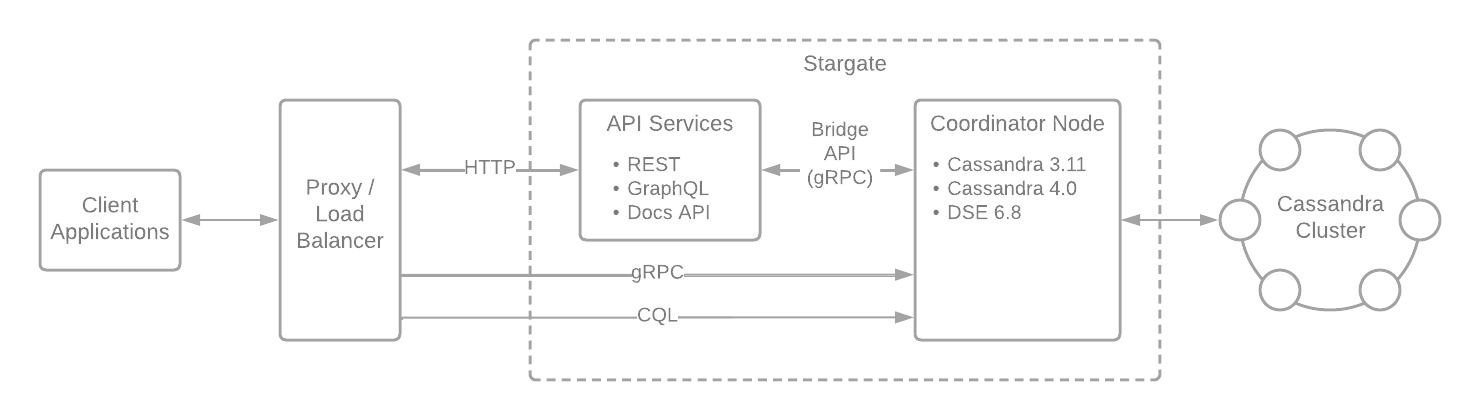
Stargate v2.0
Stargate v2.0 architecture
Stargate contains the following components:
-
API Services: Responsible for defining the API, handling and converting requests to db queries, dispatching to persistence, returning and serving response
-
cql: API implementation for the Cassandra Query Language
-
restapi: API implementation for exposing Cassandra data over REST
-
graphql API: API implementation for exposing Cassandra data over GraphQL
-
gRPC API: API implement for explosing Cassandra data over gRPC
-
-
Persistence Services: Responsible for implementing the coordination layer to execute requests passed by API services to underlying data storage instances.
-
persistence-api: Interface for working with persistence services
-
persistence-common: Utilities shared by the persistence services
-
persistence-cassandra-3.11: Joins C* 3.11 cluster as coordinator-only node (does not store data), mocks C* system tables for native driver integration, executes requests with C* storage nodes using C* QueryHandler/QueryProcessor, converts internal C* objects and ResultSets to Stargate Datastore objects.
-
persistence-cassandra-4.0: (same as above but for Cassandra 4.0)
-
-
Authentication Services: Responsible for authentication to Stargate
-
auth-api: REST service for generating auth tokens
-
auth-table-based-service: Service to store tokens in the database
-
authentication: Interface for working with auth providers
-
Stargate v1.0
Stargate v1.0 architecture
Stargate is broken up into modules that fit into three broad categories:
-
API extensions
-
Persistence extensions
-
Authentication extensions.
The diagram below shows how these modules fit together.
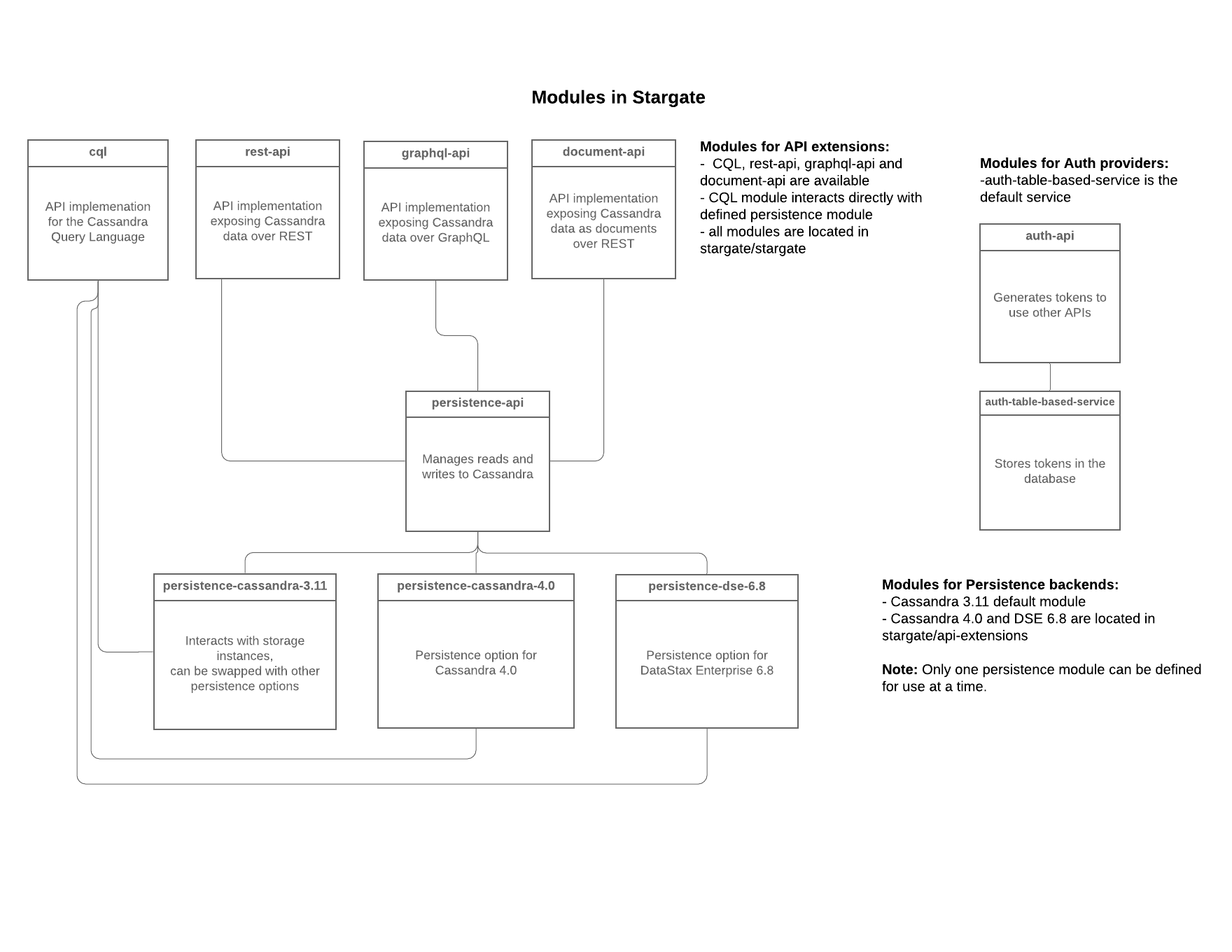
API extensions are responsible for defining the API, handling and converting requests to database queries, dispatching requests to persistence services, and returning and serving response to clients. There are currently extensions for the Cassandra Query Language (CQL), and REST and GraphQL APIs for CRUD access to data in tables with many more coming soon. These extensions use both the Authentication Extensions and the Persistence Extensions.
The REST API uses the auth-api to handle token access to the endpoints that are exposed by the Jetty-based Web Server. The GraphQL API also uses the token created with REST in the GrahpQL http header request to access the endpoints. The persistence-api is used to dispatch converted requests to the underlying storage engine. In the case of the REST API, you can see what this looks like in the RowsResource.
Persistence extensions are responsible for implementing the coordination layer to execute requests passed by API services to underlying data storage instances. The Persistence extensions are currently Cassandra-centric as Cassandra is the first database we chose to implement. The extensions for Cassandra 3.11 and 4.0 use Cassandra’s coordinator concept and code to do the majority of the work.
Specifically, when using Stargate with one of Cassandra extensions Stargate nodes:
-
join the Cassandra ring as a coordinator node, a node that does not store data.
-
mock Cassandra system tables for native driver integration.
-
execute requests with Cassandra storage instances using Cassandra’s internal
QueryHandlerandQueryProcessor. -
convert internal Cassandra objects and
ResultSetsto Stargate Datastore objects.
Authentication extensions are responsible for access control to Stargate’s APIs. Currently there’s only an auth table-based service which stores generated access tokens in the database.
These extensions are used by the API Extensions to federate access.
You can see an example of this in the REST API which requires a token to be passed to requests using the X-Cassandra-Token header. The GraphQL API and the Document API use the same token.